Wire Mesh Conveyor Belts Material
Wire mesh conveyor belts are conveyor belts made from interwoven metal wires, often used in various industrial applications due to their strength, durability, and resistance to corrosion and high temperatures. The material for these belts is typically chosen based on the specific requirements of the application, such as resistance to heat, corrosion, or mechanical wear.
Stainless Steel:
SUS304:
Characteristics: Good corrosion resistance, strength, and formability. It is non-magnetic and maintains its properties across a wide temperature range.
Applications: Ideal for food processing, pharmaceutical, and chemical industries where corrosion resistance is essential.
SUS316:
Characteristics: Superior corrosion resistance, especially in acidic or salty environments, and high-temperature strength.
Applications: Used in more corrosive environments, such as food processing (especially involving salt or acids), marine applications, and chemical processing.
SUS314:
Characteristics: Excellent oxidation resistance at high temperatures, with good mechanical properties.
Applications: High-temperature applications, such as heat treatment, annealing, and furnace conveyors.
SUS410:
Characteristics: Moderate corrosion resistance with good hardness and strength. It is magnetic and can be hardened by heat treatment.
Applications: Suitable for applications requiring moderate corrosion resistance and higher strength, such as industrial drying or washing processes.
Carbon Steel:
Characteristics: High strength and durability, cost-effective, but prone to rust if not coated or treated properly.
Applications: Used in applications where cost is a concern, and the environment is dry or where a protective coating can be applied, such as in packaging or assembly line conveyor systems.
High-Carbon and Alloy Steels:
Characteristics: Enhanced wear resistance and strength due to higher carbon content and alloying elements such as manganese, chromium, or nickel.
Applications: Used in heavy-duty applications, such as mining, material handling, and aggregate processing.
High-Temperature Alloys:
Inconel: A nickel-chromium-based superalloy known for its excellent oxidation and corrosion resistance at high temperatures.
Cr20Ni80 (Chromel, NiCr 80/20 Alloy): A nickel-chromium alloy with high resistance to oxidation and high-temperature strength.
Applications: Suitable for applications that require exposure to extreme temperatures, such as heat treatment furnaces, baking ovens, and chemical processing.
Galvanized Steel:
Characteristics: Carbon steel coated with a layer of zinc to provide corrosion resistance.
Applications: Used in applications where cost is a concern, and there is a need for moderate corrosion resistance, such as in outdoor or humid environments.
Monel (Nickel-Copper Alloy):
Characteristics: Excellent resistance to corrosion, especially in acidic and alkaline environments.
Applications: Used in highly corrosive environments, such as in chemical processing, marine applications, and food processing involving acids.
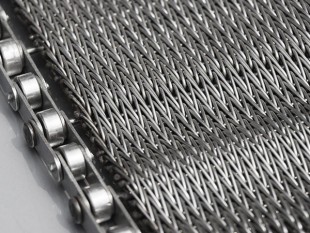
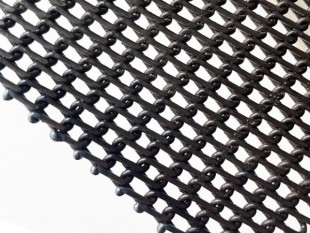
Types of Wire mesh conveyor belts

|
|

|
Balanced Spiral Woven Conveyor Belts
|
Compound Weave Conveyor Belts
|
Chain Link Conveyor Belts
|

|

|

|
Flexible Rod Conveyor Belts
|
Flat Flex Conveyor Belts
|
Eye Link Conveyor Belts
|

|

|
|
Honeycomb Conveyor Belts
|
Plate Link Conveyor Belts
|
Biscuit Baking Belts
|

|
|
|
Ladder Conveyor Belts
|
|
|
For more details please visit our website:www.industrialconveyorbelt.com
Considerations When Choosing Wire Mesh Conveyor Belts
Choosing the right wire mesh conveyor belt is crucial for ensuring efficient operation, longevity, and product quality in various industrial applications. Here are the key considerations when selecting wire mesh conveyor belts:
1. Material Selection
Corrosion Resistance: Select materials that offer resistance to corrosion, especially in environments exposed to moisture, chemicals, or acidic conditions. Stainless steels like SUS304 and SUS316 are commonly used for their excellent corrosion resistance.
Temperature Resistance: Choose materials that can withstand the operating temperatures of the application. High-temperature alloys like SUS314 or Inconel are suitable for heat treatment or furnace operations.
Wear and Abrasion Resistance: For applications involving abrasive materials or heavy loads, select materials with high wear resistance, such as high-carbon steel or certain stainless steel grades.
2. Belt Type and Weave Design
Balanced Weave: Offers a flat surface with a high degree of stability and is suitable for most applications, including food processing, drying, and heat treatment.
Compound Balanced Weave: Provides a denser mesh for smaller parts or where finer filtration is needed, such as in baking or parts cleaning.
Flat Wire Belts: Provide an open area and smooth surface, ideal for cooling, drying, and baking applications where airflow or liquid drainage is needed.
Chain Driven Belts: Designed for heavy-duty applications requiring a strong drive force and precise belt tracking, such as in automotive or industrial processing.
Spiral Weave Belts: Offer flexibility and are suitable for spiral conveyors used in freezing or cooling processes.
3. Load Capacity
Tensile Strength: Ensure the wire mesh belt has sufficient tensile strength to handle the weight and type of products being conveyed.
Deflection: The belt should not sag or deflect excessively under load, which could affect the product's stability or process efficiency.
Impact Resistance: Consider belts that can withstand impact if the application involves dropping or loading heavy items onto the belt.
4. Operating Environment
Temperature Range: Choose a belt material and design that can withstand the temperature range of the application, whether it's for freezing, baking, or high-temperature heat treatment.
Chemical Exposure: If the belt will be exposed to chemicals, choose a material resistant to chemical corrosion or degradation.
Hygienic Requirements: For food processing, pharmaceutical, or medical applications, select belts that are easy to clean, non-contaminating, and comply with sanitary standards.
5. Belt Speed and Motion
Conveyor Speed: Consider the required conveyor speed and ensure the belt can operate smoothly at that speed without excessive wear or noise.
Belt Flexibility and Articulation: The belt should have the necessary flexibility to navigate bends, curves, or inclines without stretching or breaking.
6. Maintenance and Longevity
Ease of Maintenance: Choose belts that are easy to repair, maintain, and replace. Consider belts with modular designs or easily replaceable sections.
Durability: Ensure the belt material and design are durable enough to withstand the operating conditions, minimizing downtime and replacement costs.
7. Product Compatibility
Product Type and Size: Ensure the belt's mesh size and surface are compatible with the product being conveyed. For example, finer mesh belts are suitable for small parts or powders, while larger mesh or flat wire belts are ideal for larger items.
Non-Marking and Smooth Surface: In applications where product integrity is critical (such as in food or electronics), select belts with non-marking, smooth surfaces to prevent damage or contamination.
8. Belt Tracking and Drive Mechanism
Belt Tracking: Ensure the belt is designed to stay aligned on the conveyor without shifting or drifting, which could cause damage or require frequent adjustments.
Drive Mechanism Compatibility: Choose belts compatible with the existing drive mechanism, whether it’s friction-driven, chain-driven, or sprocket-driven.
9. Compliance and Standards
Industry Standards: Ensure the belt meets the required industry standards, such as FDA, USDA, or ISO standards, especially for food processing or pharmaceutical applications.
Safety Standards: Consider belts with safety features such as smooth edges or protective coatings to prevent accidents or injuries.
Benefits of PFM Screen Wire Mesh Conveyor Belts
1. High-Quality Material Options:
Durable
Construction: Made from high-quality materials like stainless steel (e.g.,
SUS304, SUS316) and high-temperature alloys (e.g., SUS314, Inconel), PFM Screen
wire mesh conveyor belts offer excellent durability and longevity.
Corrosion
Resistance: The use of corrosion-resistant materials such as stainless steel
ensures the belts can withstand harsh environments, including exposure to
moisture, chemicals, and acidic or alkaline substances.
2. Temperature Resistance:
Wide
Operating Temperature Range: These belts are designed to function in extreme
temperature conditions, from very low (freezing) to very high (up to 1150°C or 2102°F), making them suitable for
applications like baking, freezing, heat treatment, and other high-temperature
processes.
3. Versatility in Applications:
Multiple
Weave Styles: PFM Screen offers various weave styles (e.g., balanced weave,
compound balanced weave, flat wire belts, chain-driven belts), catering to
different application needs such as cooling, drying, washing, sorting, and food
processing.
Adaptability: Suitable for a wide range of industries, including food processing,
pharmaceutical, chemical, automotive, and textile industries, due to their
versatility in design and material.
4. Enhanced Airflow and Drainage:
Open
Mesh Design: The open mesh construction allows for excellent airflow and
drainage, ideal for processes requiring cooling, drying, washing, or draining.
This feature is particularly beneficial in applications like food processing,
where quick cooling or drying is needed.
5. Ease of Maintenance and Cleanability:
Hygienic
Properties: Stainless steel wire mesh belts are easy to clean and sanitize,
making them suitable for food and pharmaceutical industries where hygiene is
crucial.
Low
Maintenance: The robust construction and resistance to wear and tear reduce the
need for frequent maintenance, resulting in lower downtime and operational
costs.
6. Precision and Stability:
Accurate
and Stable Conveyance: The high-quality manufacturing process ensures precise
belt geometry and stability during operation, providing consistent and reliable
conveyance of products with minimal slippage or misalignment.
Smooth
Surface: Certain weave styles offer smooth surfaces that are gentle on delicate
products, reducing the risk of product damage or contamination.
7. Customizability:
Tailored
Solutions: PFM Screen can customize wire mesh conveyor belts to meet specific
requirements, such as custom sizes, shapes, and designs, tailored to unique
operational needs and constraints.
Special
Coatings and Treatments: Options for special coatings or surface treatments
enhance specific properties like non-stick surfaces or increased resistance to
certain chemicals.
8. Energy Efficiency:
Low
Friction and Reduced Power Consumption: The design of PFM Screen wire mesh
conveyor belts minimizes friction, which helps reduce power consumption,
leading to more energy-efficient operation and lower operational costs.
9. High Load Capacity:
Robust
Design for Heavy Loads: These belts can handle heavy loads without stretching
or deforming, making them ideal for applications requiring high load capacity,
such as automotive parts or bulk material handling.
10. Improved Safety Features:
Safe Edges and Construction: Designed with safety in mind, these belts can
feature safe edges and smooth surfaces to reduce the risk of injuries to
operators or damage to the conveyed products.
Wire Mesh Conveyor Belts Applications
Wire mesh conveyor belts are versatile and widely used in numerous industries due to their durability, flexibility, and ability to handle various environmental conditions. The design and material properties of wire mesh belts make them suitable for applications involving high temperatures, corrosive environments, heavy loads, and processes requiring ventilation or drainage.
1. Food Processing Industry:
Baking and Cooling: Wire mesh belts are ideal for ovens and cooling conveyors due to their ability to withstand high temperatures and allow for airflow, ensuring even baking and cooling of products like bread, pastries, cookies, and snacks.
Frying: Used in deep-frying processes where belts must withstand high temperatures and exposure to oil, such as for frying chips, nuggets, and other fried foods.
Freezing: Spiral and straight-running wire mesh belts are used in freezing applications, such as in spiral freezers for quick-freeze processes for vegetables, fruits, seafood, and ready-to-eat meals.
Washing and Draining: Ideal for applications where products need to be washed, drained, or dried, such as in vegetable and fruit processing, where the open mesh allows for efficient water drainage and air drying.

2. Heat Treatment and Metal Processing:
Annealing and Hardening: Wire mesh belts can withstand extreme temperatures and are used in furnaces for annealing, hardening, and other heat treatment processes of metal parts.
Sintering: Used in sintering ovens where metal powders are heated to form solid metal components.
Quenching: Employed in quenching operations where metal parts are rapidly cooled after heat treatment, requiring belts that can withstand thermal shock.

3. Pharmaceutical and Medical Industries:
Sterilization: Wire mesh belts are used in sterilizing equipment where pharmaceutical products or medical instruments are subjected to high-temperature steam or hot air for sterilization.
Drying and Coating: Utilized in drying or coating processes where uniform airflow and even heat distribution are critical.
4. Automotive and Aerospace Industries:
Parts Washing and Drying: Wire mesh conveyor belts are used for washing and drying automotive parts due to their ability to handle heavy loads and exposure to water, detergents, and other cleaning chemicals.
Heat Treatment of Components: Used in heat treatment processes like carburizing, annealing, and tempering of automotive and aerospace components, where the belts need to withstand high temperatures and mechanical stress.

5. Electronics and Electrical Components:
Wave Soldering and PCB Assembly: Wire mesh belts are used in wave soldering machines for printed circuit board (PCB) assembly, where they can withstand high temperatures and provide precise conveyance of electronic components.
Cleaning and Coating: Suitable for processes involving the cleaning and coating of electronic components, where chemical resistance and non-reactivity are required.

6. Glass and Ceramic Industries:
Glass Annealing: Used in annealing lehrs for glass manufacturing, where the belts need to handle high temperatures and provide smooth, even transport of delicate glass items.
Ceramic Firing: Employed in kilns for firing ceramics, where the belts must endure high temperatures and provide consistent conveyance of ceramic pieces through the heating process.

7. Chemical and Fertilizer Industry:
Drying and Cooling: Used in the drying and cooling of chemicals, fertilizers, and other materials where exposure to high temperatures and corrosive chemicals is common.
Screening and Filtering: Wire mesh belts can be used in applications where fine screening or filtering of powders and granules is required.
8. Textile and Printing Industries:
Dyeing and Finishing: Wire mesh conveyor belts are used in textile dyeing, printing, and finishing processes, where they provide excellent drainage and airflow for rapid drying.
Screen Printing: Used in screen printing operations to convey fabrics or paper through drying ovens.
9. Mining and Quarrying:
Material Handling: Wire mesh belts are used in conveyors that transport heavy, abrasive materials such as ore, coal, and gravel, requiring belts with high tensile strength and resistance to wear.
10. Waste Management and Recycling:
Sorting and Conveyance: Used in recycling facilities for sorting and conveying various materials, such as plastics, metals, and glass, due to their durability and ability to handle diverse materials.
Incineration and Waste Treatment: Suitable for use in waste treatment plants, particularly in incineration processes where the belts must withstand high temperatures and corrosive byproducts.

Products Show













